6 Week Surgical Tech Program
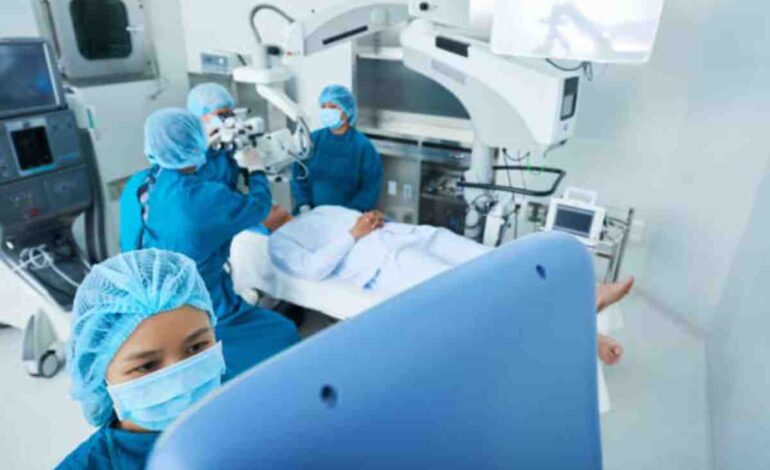
Radiologist technicians perform essential diagnostic imaging procedures and scans to help radiologists and physicians better understand patients’ health conditions. If this sounds stimulating to you, consider pursuing this health care career. Understanding the various requirements can help prepare you for success as a radiology tech.
In this article, we deliberate what a radiologist technician does, how to become one, the required skills and frequently asked questions about the role.
What is a Radiologist Technician?
A radiologist technician, also known as a radiographer, X-ray technician, radiology technologist and radiologic tech, is a health care specialist who uses X-ray and other medical imaging technologies to help health care providers make diagnoses. They position patients and properly shield them with radiation protection to obtain these images. With additional training, they may administer radiation to treat cancer and other diseases.
What does a Radiologist Technician do?
Radiographers may practice general radiography or specialize in various medical imaging techniques. They work with doctors and radiologists to produce detailed images.
Other radiologist tech tasks typically include:
- Preparing patients by explaining the procedures and asking them to remove jewelry and clothing items, as individuals can’t wear anything with metal during testing.
- Performing tests such as mammograms, X-ray exams or MRI scans.
- Reviewing patients’ histories, charts and doctors’ reports.
- Calibrating machines and positioning patients for accurate image production.
- Following safety protocols and using shielding devices to avoid exposing themselves, patients or coworkers to radiation.
- Checking the clarity of images and relaying them to the doctor.
- Sterilizing and storing imaging equipment according to the correct procedure.
- Controlling equipment to ensure radiographs are of accurate contrast, detail and density.
- Staying up-to-date on radiation safety measures and protection devices.
- Complying with state and federal government regulations and their medical institutions’ policies.
Radiologist tech specializations
Radiology technologists work in several specializations, including:
- X-rays
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Mammography
- Cardiac-interventional radiography
- Nuclear medicine
- Sonography
- Bone densitometry
- Vascular interventional radiography
How to Become a Radiologist Technician
Follow these four steps to become a radiologist technician:
1. Earn a Diploma or Equivalent
Earn a high school diploma or pass the General Education Development (GED) test. Consider taking classes in math, biology, chemistry or physics. A solid background in these subjects can help you succeed in advanced education classes. Additionally, consider volunteering at a health care center to understand the work environment better.
2. Complete an accredited radiology program
Many medical facilities and employers require radiologist technicians to have formal educational credentials from a hospital-based or college-centered program accredited by the Joint Review Committee on Education in Radiologic Technology (JRCERT). A two-year associate degree in radiography is a minimum qualification for an entry-level position. A bachelor’s or master’s degree in one of the radiologic sciences is typically required for supervisory, administrative or teaching positions. Classroom instruction may focus on topics such as:
- Patient care
- Human anatomy
- Imaging and procedures
- Radiographic pathology
- Radiologic physics
- Medical images and ethics
Students then complete clinical training at a designated hospital, clinic or diagnostic center. Their educational institute may arrange for training placements. Once students finish clinical work, they can obtain qualifications to work in health care facilities.
3. Pass a Radiographer Certification Exam
States and employers require either a state board license, American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) certification or both. ARRT requires you to have a bachelor’s degree from an accredited program, have no felony or misdemeanor convictions and meet its ethics requirements. Meeting ARRT’s education requirements and passing a voluntary certification exam are part of the certification process.
To maintain your certification, complete continuing education courses in radiography every two years. For further training, consider pursuing certificate programs in advanced imaging fields such as:
- Nuclear medicine technology
- Radiation therapy
- Mammography
- CT
- MRI
- Cardiovascular interventional technology
4. Prepare a Resume and Apply for Jobs
An effective resume might enhance your chances of getting an interview and a job. On your resume, include a concise, professional summary and why you’re right for the job. List your educational background, skills, experience and certification. Tailor it to the job requirements and highlight any additional radiology technologist skills you might have that can benefit the organization.
Relaed Pages:
